Area measurement in agricultural and forest land subsidized by EU grants
Effective measurement of land area requires advanced measuring technology. In the measurement of agricultural land are mostly used systems based on measurement of GPS points by GNSS equipment. This approach provides sufficient accuracy, if good quality of signal reception coming from satellite. Unlike, when measuring forest land the quality of signal received by GPS device is commonly problematic. In support of this issue, the technology used for forest land area measurement can be independent of the GPS signal. This may be a laser range-finder with integrated inclinometer and electronic compass device (RIC).
Benefits associated with the use of laser rangefinder compared to GPS
Historically, agricultural lands were established in favorable conditions and vice versa forests had been kept in more remote areas. Dense forest cover and presence of obstacles further limits the accessibility. Treetops and underbrush or any steep slope screen GPS antenna and significantly impair or completely restrict the reception of satellite signal. A laser range-finder with integrated inclinometer and electronic compass device (RIC) guarantees mapping in local coordinate system. Georeferencing in the proper map projection system is then solved by taking one or more GPS reference point/s on the forest boundary or in its vicinity, in any place with good reception (clearings, forest roads, etc.). Working with RIC also eliminates the necessity to measure directly along the plot border which can be alternatively measured from any point in the vicinity.
Technology
IFER – Monitoring and Mapping Solutions, Ltd. (IFER-MMS) is the developer of Field-Map. The key components of this technology for its application for measurement of agricultural and forest land area are the real-time GIS software Field-Map and the laser rangefinder TruPulse 360.

Fig. 1 Field-Map hardware set with TruPulse used for testing
.
Field-Map is a GIS mobile system including the software application Field-Map, field computer (Windows OS) and electronic measuring devices.
Field-Map software provides all necessary functionality for measuring and attributing GIS data (point, polygon, lines and other forestry oriented layers). This software allows communication with the measuring devices, registration of collected data and continuous visualization and navigation in the field. Data communication between measuring devices and field computer is ensured either via Bluetooth or via serial cable.
TruPulse 360 is a compact laser range-finder with integrated inclinometer and electronic compass device (RIC) produced by Laser Technology, Inc. (LTI). This device allows to measure distances up to 1000 m with accuracy ± 30 cm, azimuth with accuracy ± 1° and inclination with accuracy ± 0.25 °. Distances on slopes are automatically converted to horizontal distance. Measuring equipment also consists of accessories as telescopic monopod with frame and brackets for mounting field computer and TruPulse, poles with reflectors, and batteries. The basic hardware configuration weighs approximately 2.5-3 kg depending on the weight of the filed computer chosen.
Testing methodology
The accuracy of Field-Map technology including TruPulse was verified by a test based on the EU methodology for verification of technologies suitable for measurement of agricultural and forest land area. Detailed description of the testing and data processing methodology is available at the website of the Joint Research Centre (JRC), Institute for Environment and Sustainability, section GNSS equipment-validation.
Testing was carried out on 6 polygons of various sizes and shapes. The boundary of testing polygons was clearly marked on the ground (1 fixed picket every 25 m along the polygon perimeter). Reference values of area and perimeter were ensured by independent geodetic measurements with the total station Leica TRC 307. Each polygon had been tested repeatedly (9 series, 4 repetitions) with Field-Map technology including TruPulse by 3 teams of 2 operators each. Boundary lines of measured polygons were closed by using the Bowditch transformation. Resulting area and perimeter were calculated automatically by Field-Map software.

Fig. 2: Overview map of the testing polygons in Radlik, Czech Republic
Results
The European restrictions on land measurement subsidized by EU grants allow a maximum positional error expressed in the form of buffer width of the measured area. For forest land the error is set at maximum 3 m and for agricultural land at maximum 1.5 m. The responsible EU institution Join Research Centre, after verifying the testing and the data analysis carried out by IFER-MMS staff, found the mean reproducibility of the testing to be 0.34 meters. This result validates the efficiency of the Field-Map technology including TruPulse putting this technology into the highest class of accuracy.
For more information please contact: Pavel Malek, email: pavel.malek@ifer.cz, tel.: +420 241 950 607

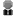 User login
User login